Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to clone an object using the clone keyword in PHP.
To clone an object is to create a copy of an object. The clone keyword allows you to perform a shallow copy of an object. By combining the clone keyword and __clone() magic method, you can perform a deep copy of an object.
It’ll be easier to understand the clone, shallow copy, and deep copy concepts via examples.
Setting up #
The following example defines a simple Person class that has one property $name. To make it simple, we’ll make the $name property public:
<?php
class Person
{
public $name;
public function __construct($name)
{
$this->name = $name;
}
}Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Copying object via assignment #
The following illustrates how to copy an object via the assignment opeator:
<?php
class Person
{
public $name;
public function __construct($name)
{
$this->name = $name;
}
}
$bob = new Person('Bob');
// assign bob to alex and change the name
$alex = $bob;
$alex->name = 'Alex';
// show both objects
var_dump($bob);
var_dump($alex);Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Output:
object(Person)#1 (1) {
["name"]=> string(4) "Alex"
}
object(Person)#1 (1) {
["name"]=> string(4) "Alex"
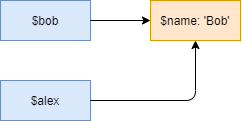
}Code language: PHP (php)The var_dump() shows one object with the #1.
How it works.
- First, create a new instance of the
Personclass called$bobwith the$nameproperty sets to'Bob'. - Second, assign
$bobto$alexand change the value of the$nameproperty to'Alex'. - Third, use the
var_dump()function to show both objects.
In this example, both $bob and $alex reference the same object in the memory. When we change the property of an object, it reflects in both references.
Copying object using the clone keyword #
PHP provides you with the clone keyword that allows you to create a shallow copy of an object. For example:
$bob = new Person('Bob');
// clone an object
$alex = clone $bob;
$alex->name = 'Alex';
// show both objects
var_dump($bob);
var_dump($alex);Code language: PHP (php)Output:
object(Person)#1 (1) {
["name"]=> string(3) "Bob"
}
object(Person)#2 (1) {
["name"]=> string(4) "Alex"
}Code language: PHP (php)In this example, the clone keyword creates a copy of the Person object. There are two objects in the memory. Therefore, changing the property of one object doesn’t affect the other:
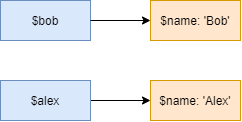
The var_dump() also shows the object #1 and #2.
PHP __clone magic method #
The __clone() is a magic method with the following syntax:
function __clone ( ) : voidCode language: JavaScript (javascript)If you define the clone() method, PHP will execute it automatically when the cloning completes. The clone() is useful when you want to change the properties of the copied object.
Shallow copy #
As mentioned ealier, the clone performs a shallow copy of an object. It means that:
- Create a copy of all properties of an object.
- If a property references another object, the property remains a reference.
In other words, when an object has a property that references another object, that property remains a reference after cloning.
Let’s see the following example:
<?php
class Address
{
public $street;
public $city;
}
class Person
{
public $name;
public $address;
public function __construct($name)
{
$this->name = $name;
$this->address = new Address();
}
}Code language: HTML, XML (xml)In this example:
- First, define a new class called
Addressthat has two properties$cityand$street. - Second, change the
Personclass by adding theaddressproperty. In the constructor, initialize theaddressto a newAddressobject.
The Person class has the address property as a reference.
The following creates a new Person object called $bob and assigns the properties of the address property:
$bob = new Person('Bob');
$bob->address->street = 'North 1st Street';
$bob->address->city = 'San Jose';
var_dump($bob);Code language: PHP (php)Output:
object(Person)#1 (2) {
["name"]=> string(3) "Bob"
["address"]=> object(Address)#2 (2) {
["street"]=> string(16) "North 1st Street"
["city"]=> string(8) "San Jose"
}
}Code language: PHP (php)The var_dump() shows two objects Person (#1) and Address(#2). The Person object has the address property that references the Address object.
The following creates a copy of the $bob object and assigns it to $alex. It also changes the value of the $name property to 'Alex':
$alex = clone $bob;
$alex->name = 'Alex';
var_dump($alex);Code language: PHP (php)Output:
object(Person)#3 (2) {
["name"]=> string(4) "Alex"
["address"]=> object(Address)#2 (2) {
["street"]=> string(16) "North 1st Street"
["city"]=> string(8) "San Jose"
}
}Code language: PHP (php)The var_dump() shows the new Person object (#3) which is a copy of the Person object (#1). However, the address property of the new Person object still references the same Address object:

It means that both Person objects have the address property that references the same Address object. Changing the Address object from $alex will affect $bob:
$alex->address->street = '1 Apple Park Way';
$alex->address->city = 'Cupertino';
var_dump($bob);Code language: PHP (php)Output:
object(Person)#1 (2) {
["name"]=> string(3) "Bob"
["address"]=> object(Address)#2 (2) {
["street"]=> string(16) "1 Apple Park Way"
["city"]=> string(9) "Cupertino"
}
}Code language: PHP (php)Put it all together:
<?php
class Address
{
public $street;
public $city;
}
class Person
{
public $name;
public $address;
public function __construct($name)
{
$this->name = $name;
$this->address = new Address();
}
}
$bob = new Person('Bob');
$bob->address->street = 'North 1st Street';
$bob->address->city = 'San Jose';
var_dump($bob);
$alex = clone $bob;
$alex->name = 'Alex';
var_dump($alex);
$alex->address->street = '1 Apple Park Way';
$alex->address->city = 'Cupertino';
var_dump($bob);Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Deep copy with __clone method #
Deep copy creates a copy of an object and recursively creates a copy of the objects referenced by the properties of the object.
Since PHP calls the __clone() method automatically after cloning an object, you can clone the objects referenced by the properties of the class.
The following example illustrates how to use the __clone() magic method to carry a deep copy of the Person object:
<?php
class Address
{
public $street;
public $city;
}
class Person
{
public $name;
public $address;
public function __construct($name)
{
$this->name = $name;
$this->address = new Address();
}
public function __clone()
{
$this->address = clone $this->address;
}
}
$bob = new Person('Bob');
$bob->address->street = 'North 1st Street';
$bob->address->city = 'San Jose';
$alex = clone $bob;
$alex->name = 'Alex';
$alex->address->street = '1 Apple Park Way';
$alex->address->city = 'Cupertino';
var_dump($bob);
var_dump($alex);
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Output:
object(Person)#1 (2) {
["name"]=> string(3) "Bob"
["address"]=> object(Address)#2 (2) {
["street"]=> string(16) "North 1st Street"
["city"]=> string(8) "San Jose"
}
}
object(Person)#3 (2) {
["name"]=> string(4) "Alex"
["address"]=> object(Address)#4 (2) {
["street"]=> string(16) "1 Apple Park Way"
["city"]=> string(9) "Cupertino"
}
}Code language: PHP (php)The new here is __clone() method in the Person class. The __clone() method create a copy of the Address object.
Deep copy using serialize and unserialize functions #
Another way to carry a deep copy of an object is to use the serialize() and unserialize() functions.
The serialize() function creates a storable representation of an object while the unserialize() function creates an object from the storable value.
The following deep_clone() function creates a deep copy of an object:
<?php
function deep_clone($object)
{
return unserialize(serialize($object));
}Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Summary #
- Use
cloneto perform a shallow copy of an object. - Combine
cloneand__clone()method to create a deep copy of an object.