Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn about cookies and how to use the PHP setcookie() function to manage cookies effectively.
Introduction to cookies #
The web works based on the HTTP protocol. The HTTP protocol is stateless.
When a web browser requests a page from a web server, the web server responds with the page content. Later, the same web browser requests the same page again, and the web server has no information that the request is from the same web browser.
Cookies solve this stateless challenge.
A cookie is a piece of data a web server sends to the web browser. The browser may store it and send it back in subsequent requests to the same web server. By using the same cookie, the web server knows that two requests come from the same web browser.
Cookies are also known as web cookies, HTTP cookies, or browser cookies. We’ll use the cookies to make it short.
The following flow chart illustrates how cookies work:
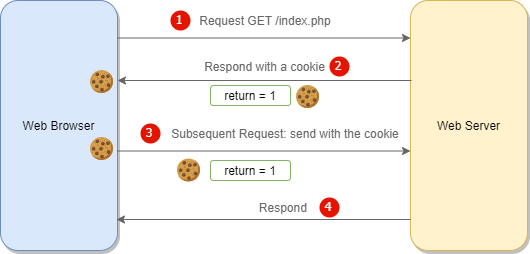
How it works.
- First, the web browser sends a request to the web server. The web server doesn’t have any information about the web browser. The web server creates a cookie with a name return and a value 1 and attaches the cookie to the HTTP response header. To create a cookie, you’ll use the
setcookie()function. - Second, the web browser stores the cookie.
- Third, the web browser sends the second request with the stored cookie in the header of the HTTP request to the web server. On the web server, PHP can access the cookie via the
$_COOKIEsuperglobal variable and do something accordingly. - Finally, the web server responds with the content of the request. Typically, it responds to the web browser with the content based on the value of the cookie.
A web browser can store a cookie with a maximum size of 4KB, but this limit varies between browsers.
A cookie has an expiration date. Typically, web browsers store cookies for a specific duration, and the web server can specify the expiration time for a cookie.
A cookie also stores the web address (URL) that indicates the URL that created the cookie. The web browser can send back the cookie that was originally set by the same URL. In other words, a website won’t be able to read a cookie set by other websites.
Most modern web browsers allow users to choose to accept cookies. Therefore, you should not wholly rely on cookies for storing critical data.
Why using cookies #
In general, websites use cookies to enhance user experiences. For example, you would have to log in to a website again after you leave it without cookies.
Typically, you’ll use cookies for the following purposes:
- Session management: cookies allow a website to remember users and their login information or anything else the web server should remember.
- Personalization: cookies can store user’s preferences, themes, and other settings.
- Tracking: cookies store user behavior. For example, on an E-commerce website, you can use cookies to record the products that users previously viewed. Later, you can use this information to recommend the related products that users might be interested in.
Setting a cookie in PHP #
PHP makes it easy to work with cookies using the setcookie() function. The setcookie() function allows you to send an HTTP header to create a cookie on the web browser.
<?php
setcookie (
string $name ,
string $value = "" ,
int $expires = 0 ,
string $path = "" ,
string $domain = "" ,
bool $secure = false ,
bool $httponly = false
): boolCode language: PHP (php)The following table illustrates the arguments of the setcookie() function:
| Argument | Meaning |
|---|---|
| $name | The name of the cookie |
| $value | The value of the cookie. It can be any scalar value, such as a string or integer. |
| $expires | The time (in a UNIX timestamp) the cookie expires. If $expires is not set or set to 0, the cookie will expire when the web browser closes. |
| $path | The path on the web server on which the cookie will be available. For example, if the path is ‘/’, the cookie will be available within the domain. |
| $domain | The domain to which the cookie will be available. |
| $secure | if $secure is set to true , the cookie should be transmitted over a secured HTTP (HTTPS) connection from the web browser. |
| $httponly | if $httponly is true, the cookie can be accessed only via the HTTP protocol, not JavaScript. |
As of PHP 7.3.0, you can use the same setcookie() function with an alternative signature:
setcookie (
string $name ,
string $value = "" ,
array $options = [] ) : boolCode language: PHP (php)The $options argument is an array that has one or more keys, such as expires, path, domain, secure, httponly and samesite. The samesite can take a value of None, Lax, or Strict. If you use any other key, the setcookie() function will raise a warning.
The setcookie() function returns true if it successfully executes. Notice that it doesn’t indicate whether the web browser accepts the cookie. The setcookie() function returns false if it fails.
$_COOKIE #
The $_COOKIE an associative array that stores the HTTP cookies. To access a cookie by a name, you use the following syntax:
$_COOKIE['cookie_name']Code language: PHP (php)If the cookie name contains dots (.) and spaces (' '), you need to replace them with underscores (_).
To check if a cookie is set, you use the isset() function:
<?php
if(isset($_COOKIE['cookie_name'])) {
}Code language: PHP (php)The $_COOKIE is a superglobal variable so that it can be accessed from anywhere in the script.
Reading a cookie #
Before reading a cookie value, you should always check if it has been set by using the isset() function:
<?php
if (isset($_COOKIE['cookie_name'])) {
// process the cookie value
}Code language: PHP (php)To check if a cookie equals a value, you use the following code:
<?php
if (isset($_COOKIE['cookie_name']) && $_COOKIE['cookie_name'] == 'value') {
// ...
}Code language: PHP (php)Deleting a cookie #
If you don’t use a cookie, you can force the browser to delete it. PHP doesn’t provide a function that directly deletes a cookie. However, you can delete a cookie using the setcookie() function by setting the expiration date to the past.
The following code deletes a cookie with the cookie_name in the subsequent page request:
unset($_COOKIE['cookie_name']);
setcookie('cookie_name', null, time()-3600);Code language: PHP (php)PHP cookie example #
The following example shows how to use a cookie to display a greeting message to a new or returning visitor.
<?php
define('ONE_WEEK', 7 * 86400);
$returning_visitor = false;
if (!isset($_COOKIE['return'])) {
setcookie('return', '1', time() + ONE_WEEK);
} else {
$returning_visitor = true;
}
echo $returning_visitor ? 'Welcome back!' : 'Welcome to my website!';Code language: PHP (php)How it works.
First, define a constant that stores one week in seconds:
define('ONE_WEEK', 7 * 86400);Code language: PHP (php)Second, set the returning_visitor to false:
$returning_visitor = false;Code language: PHP (php)Third, check the cookie with the name return. If the cookie is not set, create one with the value one and an expiration date of one week. Otherwise, set the $returning_visitor variable to true.
if (!isset($_COOKIE['return'])) {
setcookie('return', '1', time() + ONE_WEEK);
} else {
$returning_visitor = true;
}Code language: PHP (php)Finally, display the greeting message based on the value of the $returning_visitor variable.
When you request the page for the first time, you’ll see the following message:
Welcome to my website!Code language: PHP (php)If you open the web developer tool, you’ll see the cookie as shown in the following picture:
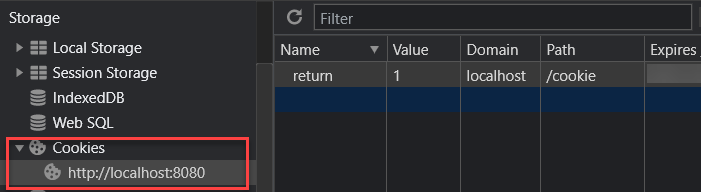
Since the web browser already stores the cookie with the name return and value 1, if you refresh the page, you’ll see a different message:
Welcome back!Code language: PHP (php)This cookie will last for seven days set by the webserver. Of course, you can manually delete the cookie from the web browser.
Summary #
- A cookie is a piece of data the web server sends to a web browser to check if two requests come from the same web browser.
- Use the PHP
setcookie()function to set a cookie sent along with an HTTP header from the web server to the web browser. - Use the superglobal variable
$_COOKIEto access the cookies in PHP.